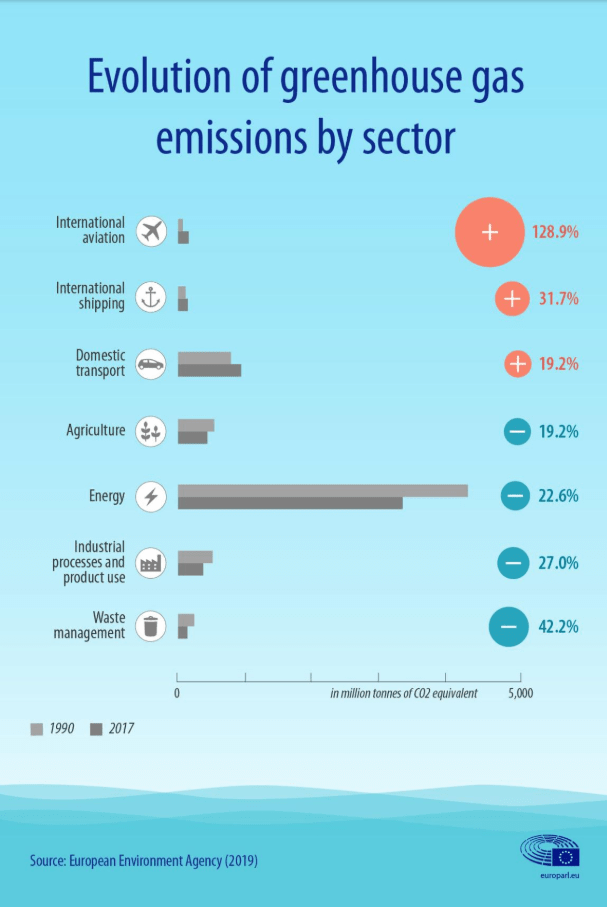
Infographics on the evolution of greenhouse gas emissions by sector
Carbon Dioxide is talked about a lot and CO2 is sometimes used as shorthand for all greenhouse gases, but GHGs are not all the same. However, CO2 is the main GHG produced by human activity.
Carbon Dioxide could last forever in the Earth's atmosphere .
Human activity such as burning fossil fuels like coal, oil or natural gas along with the burning of biomass (wood and other non fossilised plant material) produces almost all the CO2 in the Earth's atmosphere. We burn these products to fuel transport and provided energy for manufacturing, heating and cooling, and powering all our electric devices, unless we have sourced the energy from a renewable source. CO2 caused by human activity also includes wildfires deliberately started by human beings for various reasons. Deforestation and other changes in how land is used is another way human activity contributes to CO2 emissions.
Minimal CO2 emissions occur naturally caused by natural wildfires and volcanic eruptions, respiration of plants and animals, melting permafrost and even the weathering of certain rocks.
Methane appears to be the most short-lived greenhouse gas spending only about 10 years in the Earth's atmosphere, but it causes a lot more warming than CO2.
Human activity is responsible for 60% of methane in the atmosphere produced as a result of leaks from fossil fuel production and transportation, landfill, livestock digestion and manure, rice farming: natural gas, deliberate wildfires or biomass burning.
40% of methane in the Earth's atmosphere is from natural sources: plant-matter breakdown inwetlands, lakes, and ponds; naturally occurring wildfires and biomass burning; termites; the ocean: sediment and permafrost.
Nitrous Oxide lasts for about 110 years in the Earth's atmosphere and causes significantly more warming than CO2 or methane.
fuels and burning vegetation, results in about 40% of the nitrous oxide in Earth's atmosphere
60% of the methane comes from natural sources, primarily bacteria breaking down nitrogen in soil and the
ocean.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs, namely CFC-11. CFC-12, CFC-113) persist in the Earth's atmosphere for between 52 to 93 years and result in a far greater warming effect than any of the other GHGs.
All chlorofluorocarbons in the Earth's atmosphere have been produced by humans from refrigerants, solvents and spray cans containing CFCs.
In the 1990's concerns about CFCs causing a hole in the ozone layer led to a number of directives which phased them out of general use or even banned them in many countries. However, it seems they could still be in use in some parts of the world.
You can find out more here


No comments:
Post a Comment